We all know the wonderful feeling of cycling, but unfortunately it’s not always sun on the face and wind in the hair. Pedaling is a low-impact motion, making cycling one of the best ways to stay fit without putting stress on your joints. However, it’s also a highly repetitive action through a limited range of motion, which has consequences over time. Injury is a part of almost every sport, and cycling is no exception, but that doesn’t mean you need to hang up your jersey and sell your bike. Here’s what you need to know about hidden cycling injury and what you can do to fix them.
The Issue: Adaptive Muscle Shortening
Muscles do not naturally maintain their healthy or ideal range of motion on their own. In fact, it’s just the opposite, especially with the increase of 9-5 desk jobs. Muscles will change their functional resting length to adapt to the length at which they are habitually used or positioned. The process by which muscle fibres physically shorten is called “adaptive shortening.”
Cycling is one of the few activities in which muscles contract concentrically (while shortening), rather than eccentrically (while lengthening). The repetitive motion causes muscle fibres to shorten  if action is not taken. Not only will shortened muscles impact your efficiency, comfort, and aerodynamics on the bike, but they will eventually lead to injury.
if action is not taken. Not only will shortened muscles impact your efficiency, comfort, and aerodynamics on the bike, but they will eventually lead to injury.
The cycling position is, unfortunately, more time spent in a hunched over posture that can compound already tight hip flexors, weak glutes and rounded shoulders. If you’re a weekend warrior, then it really is a case of when you will suffer an injury rather than ‘if.’ When you’ve spent most the week in a relatively sedentary position, and then hit the weekend with high levels of activity, you are taking chronically shortened muscles and forcing them to fire so quickly that it can lead to joint injury.
The Symptoms: Weak and shortened hamstrings are caused by the combination of the upper section becoming loose and weak while the lower section behind the knee becomes tight and never fully extends. This can show up as either knee or hip pain.
The Fix: The problem is a little more complex than just lengthening the muscles back to their natural state. It is a combination of stretching and strengthening that can reverse the effects of adaptive shortening, as it takes both range of motion and strength to bring muscle balance.
The Issue: Lower Crossed Syndrome
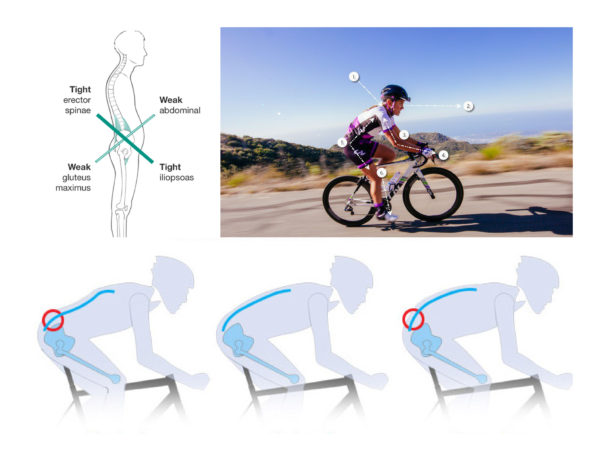
Lower Crossed Syndrome (LCS) is a neuromuscular condition in which there are both tight and weak muscles. Specifically, it refers to weak abdominal and gluteal muscles combined with tight iliopsoas and erector spinae muscles (see diagram). This is the most common underlying cause of anterior pelvic tilt, which is common among even professional cyclists.
The seat of power on a bicycle is the pelvis. When the pelvis is properly aligned the rest of the body can pedal efficiently. When the pelvis is misaligned and unstable, it is a recipe for not only lower back problems but hamstring problems too. An unstable pelvis leads to rocking. With each rock, the pelvis engages lower back muscles and hamstrings in ways that should not be involved in pedaling, overworking and straining the muscles unnecessarily.
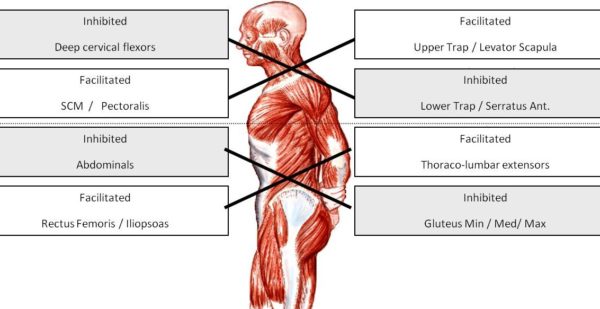
The Symptoms: LCS can become obvious in posture, as it leads to forward head posture, flat glutes, and a protruding abdomen as the pelvis tilts anteriorly (forward). The inhibited muscles, 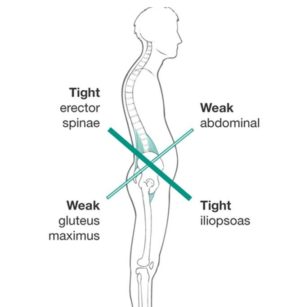 abdominals and gluteals, are never fully engaged in cycling, while the facilitated muscles, rectus femoris (quadraceps), iliopsoas and thoraco-lumbar extensors are always engaged and often overworked. Constantly engaging those lower back muscles without proper support from a stable core often results in lower back pain for cyclists.
abdominals and gluteals, are never fully engaged in cycling, while the facilitated muscles, rectus femoris (quadraceps), iliopsoas and thoraco-lumbar extensors are always engaged and often overworked. Constantly engaging those lower back muscles without proper support from a stable core often results in lower back pain for cyclists.
The Fix: The first step is to loosen the tight cross, which will quickly alleviate pain and discomfort caused by LCS. This is done this through targeting stretching, mobility movements, and foam rolling. The second step is targeted and deep stabilization exercises that will help build up the glutes and abdomen.
The Issue: Knee Pain
This one may not be so hidden, as knee pain is one of the most common injuries among athletes. In fact, a 2010 study of professional cyclists found that knee pain was the cause for over half of the time spent off the bike. As one of the most complex joints in the body, and in combination with muscle imbalance as discussed, it makes sense that it’s often one of the first places we experience pain.
To understand knee pain it is helpful to have a basic idea of what lies beneath the skin. In simplistic terms, think of the knee joint as a hinge where the quadriceps muscles pull the knee straight and the hamstring muscles bend the knee. The quadriceps run from the front of the femur (thigh bone) to the patella (knee cap). The patella acts as a pulley to increase the force generated by quadriceps which creates a greater torque on the tibia (shin bone).
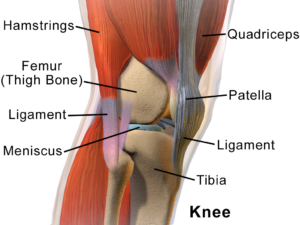 To make matters more complicated, the ITB runs down the outside of the thigh and blends into the outside of the knee. ITB stands for iliotibial band and is a well known potential source of trouble for cyclists, runners and active people in general. The ITB is also attached to your glutes (buttock muscles) and hip flexors. Often when looking for the source of knee pain we have to pay close attention to hip flexibility and control.
To make matters more complicated, the ITB runs down the outside of the thigh and blends into the outside of the knee. ITB stands for iliotibial band and is a well known potential source of trouble for cyclists, runners and active people in general. The ITB is also attached to your glutes (buttock muscles) and hip flexors. Often when looking for the source of knee pain we have to pay close attention to hip flexibility and control.
The Fix: Some types of knee pain require rest, but most are caused by muscular imbalance. Again, it takes a combination of stretching and mobility exercises to loosen tight muscles and build up the proper supporting muscles.
The Mistake Most Cyclists Make Stretching: Not Having a Plan
Most of us were taught that stretching for a couple minutes before exercise would help loosen the muscles and prevent injury, but this is not the case. Holding a static stretch for 10 seconds will do nothing to lengthen the muscle, and barely scratches the surface of what needs to happen in the structure of the muscle.
The only way to achieve muscle balance is to practice a variety of stretches over a prolonged period of time (at least 2 weeks), hold each for the appropriate amount of time, and complete in combination with some strength training.
It can be tough to accomplish all that on you own. Even with the best of intentions and a plan laid out by a physiotherapist, it’s easy to never do it at all, or stop as soon as the pain is gone. Stretching should be thought of as basic body maintenance, especially for cyclists.
As cyclists, we know how hard it is to stick to a stretching routine. We all want to spend more time on our bike, but maintaining a healthy range of motion and flexibility will, in the long run, keep you on the bike without injury. That’s why we’ve partnered with Dynamic Cyclist to bring you a stretching and strength program that is easy to follow, and is geared towards cyclists. They’re offering our readers a free 7 day trial, just click the link below to get started.
